|
|
 |
|
Surgical microscope Knowledge Summary |
 |
|
We
specialize in manufacture that Surgical
microscope (operating microscope),Dental
surgical microscope.
We sell
Dental
surgical microscope,ENT Surgical microscope
(operating microscope).
|
|
*Different
types of microscopes |
| *How
to Operate a Microscope |
| *Definition
of the
Surgical microscope |
| *About
Microscope Basics |
| *Surgery
microscope |
| *Surgical
Microscopes
Summary |
| *The
Dental Operating microscope -- A New Reality? |
| |
|
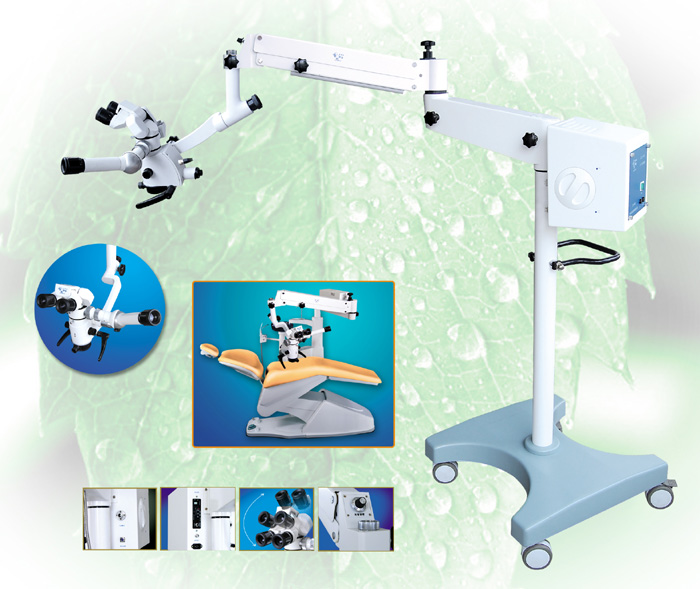
The Model LZJ-6E
Microscope Operation for ENT and Dental
(Dental surgical
microscope,dentistry,
Operation)
 |
|
The Dental Operating Microscope -- A New Reality? |
The practice of
dentistry is constantly evolving. Change in the Dental microscope
(Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope,dentistry,Operation)
environment, while being practical and useful, should be
challenging and interesting for the entire microscope (Dental
surgical microscope,operating microscope, dentistry,Operation) team.
Since the 1970s, endodontists have had a better
understanding of 'cleaning and shaping' the 'root canal
system' as opposed to just 'filing' and 'filling.' These
earlier concepts have not changed significantly with
time. However, there has been an abundance of
instruments and technology developed to better address
the root canal anatomy and provide more predictable and
successful outcomes. Consider such examples as apex
locators, rotary nickel titanium instrumentation,
thermosoftened obturation systems and more recently,
digital radiography.
While all of the above mentioned developments may
increase the speed and efficiency of performing the
originally perceived root canal treatment, the use of
magnification in dentistry has probably been the best
improvement in the last 30 or so years. Fibre optic
illumination has proven to be the perfect adjunct to
high visual magnification. Dentists (dentistry,
Operation,surgical
microscope,operating
microscope) can now treat
patients with greater certainty, and at a previously
unachieved level of quality. In endodontics, canal
orifice morphology can be better understood on the pulp
chamber floor and procedural misadventures such as
perforations can be better avoided. If procedural
accidents, such as perforations and/or separated
instruments, do occur, then they can be better managed
with the use of high visual magnification and fibre
optic illumination.
dentistry microscope (operating
microscope,Dental surgical
microscope, dentistry, Operation,surgical
microscope)
loupes are most commonly used and are available in
various magnifications. I began with 2.5X magnification,
and progressed to 4.5X magnification with comfort. I
even attempted loupes with greater than 6.5X
magnification, but only lasted approximately 30 seconds,
which was about the time it took to feel dizzy and nauseous. While the microscope
(Dental surgical microscope ,
operating microscope, dentistry, Operation) loupes are useful in lower
magnifications, the view field becomes narrowed and
strains the operator with the higher levels. In
addition, to change magnifications, you must change
loupes.
Microscopes have been available in the medical field for
many years. The next logical step for dentistry was to
combine magnification and illumination, as it presently
exists with the dentistry operation microscope (Dental
surgical microscope,operating microscope, dentistry,
Operation) (DOM). In
the mid '90s in Southern California, I attended my first
course on the use of the dentistry
microscope
with Dr. Gary Carr instructing a three day course at his
Pacific Endodontic Research Foundation (PERF). I
performed what appeared to be miracles by removing
separated instruments from the apices of curved canals
on dog molars. I came back to Toronto, bought a mobile
microscope(dentistry,
Operation) , and then watched the dust settle on the
protecting cover. I could not remain seated comfortably
for the complete procedure with the microscope (dentistry,operating
microscope, Operation). It was
frustrating and the set up time was immeasurable.
However, I did attempt, about once a month, to look for
fractures, and perform further endodontic acrobatics.
Last year we relocated our offices and installed ceiling
mounted microscopes (dentistry,
Operation) in all of our operatories. The
design was professionally done for proper function and
placement by Steve Newfield of Global dentistry microscope
(dentistry, Operation). He also provided the training. A
significant advantage exists in starting from the
basics, and then progressing cautiously and
systematically. Now I can manipulate the microscope (dentistry,Dental surgical microscope, operating microscope,Operation.) with
precise control without fear and uncertainty. I learned
that I did not have to be "rigid" and that I could work
back and forth easily, with or without the microscope. I
can look away from the optics, I can move the microscope
(Dental surgical
microscope,operating microscope, dentistry, Operation,surgical
microscope) aside and then return to the working position as before.
Since then every patient in my professional care, has
received the benefit from the microscope (dentistry,
Operation,operating
microscope,) for both
conventional and endodontic treatment. I am
constantly impressed with its many applications and
allowing me to provide care that many years ago I was
unable to provide. It is unlikely that you will hear
anything similar about the other technological
improvements and their use.
The benefits are apparent in using the surgery microscope
(dentistry,
Operation) . There
are numerous articles on how the quality of the
dentistry performed while working with the microscope
can be superior.l dentistry microscope
(Operation,Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope,dentistry), for example, can be of benefit to dentists during
examination and diagnosis. Visualizing fractures of
fillings, tooth structure, and roots has been made more
predictable. Personally, the use of the Dental (dentistry,
Operation) microscopehas
made me more efficient, which can be measured both in
time and in quality. More importantly, I am not
suffering from fatigue at the same level as before.
Using the dentistry
microscope (Dental surgical
microscope, operating microscope, dentistry,Operation) loupes and fibre-optic
head lamps, as good as they are, become a weight and
strain on the head and neck, not unlike 'a pain in the
neck'. When using the microscope (Operation,dentistry) , my spine is straight
and in a physiological position. I am not contorting my
body to look around the tooth, I am looking straight
ahead and seeing the tooth below me (of course attached
to the patient). I feel more relaxed which directly
affects my desire to continue the treatment. With proper
body position, dentist and patient, and correct focal
distance, I am able to view the working field and change
the magnification from 2.5 to 20X with ease and without
moving from the visual field.
Surgery
Microscopes (Dental surgical
microscope , operating microscope, dentistry, Operation) are included in the education in most if not
all postgraduate programs in endodontics. They are
becoming more and more part of the curriculum in
undergraduate dentistry microscope schools. Either the educators are
being responsible of their positions or the microscope
(dentistry, Operation)
manufacturers are very good at their marketing.
Dental (dentistry) surgical microscope set-ups in operatories can vary. They
can be either mobile or ceiling/wall/floor mounted and
may be set up to be accessed by two operatories.
Stability must be given to each unit depending on the
height and length of the microscope (dentistry,
Operation) arms required to
achieve the proper position.
microscope (Operation,Dental surgical microscope,operating microscope,dentistry ) permit access to additional several auxillary functions. High resolution digital still and
video cameras can be attached to the microscope. My
office has incorporated operatory and remote location
monitors, to enable audio/visual teaching to staff
members, dentists and other interested groups.
Limiting factors to the dentistry microscope (dentistry,Operation), for example,
include cost, space constraints and motivation. I would
never preach about "the return on investment" by using
the microscope (Operation,dentistry) . Personally, the impact on income has
taken a 'back' seat to the influence on my attitude and
comfort.
Once the limitations have been bypassed, a proper choice
in microscope (Dental
surgical microscope , operating
microscope,dentistry,Operation) can be
made. The company will help you, step by step, through
all the obstacles. Therefore, choose carefully. The
company will train you and your team in using the
microscope. The training should occur in stages as your
familiarity and ability evolves.For example, treating
certain teeth will either require change in the position
of the microscope, or sometimes, the position of the
patient. I have also recently been introduced to a
smaller faced Dental microscope (dentistry, Dental
surgical microscope,operating,
Operation) mirror, allowing
better access to more confined spaces.
Compare the three choices available today for
magnification and illumination:
1) No magnification and the dental overhead light
2) microscope loupes and fibre-optic head lamp illumination
3) microscope (Operation,dentistry)
In conclusion, you may decide that the status quo is
satisfactory, and there is no need for change. You may
also decide to try microscopic dentistry. Patients will
sense your excitement, appreciate the extra effort, and
recognize your desire to achieve perfection.
|
| Article Source: |
| http://www.oralhealthjournal.com/issues/story.aspx?aid=1000223096&type=Print%20Archives |
|
Back To Top |
|
Different
types of microscopes |
There are four main
types of microscopes (Operation,dentistry) that a biologist uses: dissection,
compound, Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), and
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM).
There is certain terminology used when discussing
microscopes (
Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope,dentistry,Operation.). Magnification is referring to the
ratio of the size seen in the microscope (Operation,dentistry) to the actual
size of the specimen. On a compound microscope (dentistry,Operation) it is
usually between 4x and 100x. Resolution is the clarity
and detail seen. It is the minimal distance between two
points in which they can be seen separately (i.e.: not
blurred). Field of view refers to how much you actually
see when looking in a microscope(Dental
surgical microscope,operating microscope, dentistry,
Operation) . As field of view
increases, magnification decreases. Depth of field is
the number of layers you see. Total magnification is the
product of the objective lens and the ocular (10x). Parfocal is a term used when describing compound
microscopes (dentistry,
Operation). this means that the focus is maintained
when changing the magnification. This way you don't have
to re-focus when changing powers.
A dissection microscope (dentistry,
Operation) is light illuminated. The image
that appears is three dimensional. It is used for
dissection to get a better look at the larger specimen.
You cannot see individual cells because it has a low
magnification.
A compound microscope (Operation,dentistry) is also light illuminated. The
image seen with this type of microscope (dentistry,Operation,Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope.) is two
dimensional. This microscope is the most commonly used.
You can view individual cells, even living ones. It has
high magnification (from 4x - 100x). However, it has a
low resolution.
SEM use electron illumination. The image is seen in
three dimension. It has high magnification and high
resolution. The specimen is coated in gold and the
electrons bounce off to give you and exterior view of
the specimen. The pictures are in black and white.
TEM is also electron illuminated. This gives a two
dimensional view. Thin slices of specimen are obtained.
The electron beams pass through this. It has high
magnification and high resolution.
A compound surgery microscope
(Dental surgical microscope ,
operating microscope, dentistry,Operation) contains twelve basic parts. The
ocular is the eye piece. It is what you view through. It
contains a lens of with a magnification of 10x. The
ocular is attached to the body. The body, also called
the barrel, contains a mirror to view the image at an
angel. The arm of the microscope (dentistry,
Operation)is used as a handle
when moving microscopes (Operation,dentistry) . It extends from the body to the
base (which I will discuss shortly). The nosepiece holds
the objective lens and is attached to the body. The
objective lens magnifies by the power. The mechanical
state is where the slide goes. It can be adjusted
accordingly. The diaphragm controls the amount of light.
The condenser focuses the light on the image. The light
source is whit light used to illuminate the specimen.
The coarse adjustment focuses on low powers while the
fine adjustment is used to focus on high lenses. The
base holds the light source.
To operate a microscope (dentistry,Dental
surgical microscope,operating
microscope, Operation)properly, you should follow some
simple steps. First you must plug it in and turn it on.
Make sure it is set on the lowest power. Move the stage
to the top position.
Place the slide on the stage agist the corner. Adjust
the stage. Use the coarse adjustment to get the image in
focus. Use the fine adjustment to see more detail.
Finally move the lens clockwise to move to higher
magnification. Your specimen should be seen clearly in
focus even when changing powers. |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.essortment.com/all/typesofmicrosc_rfpc.htm |
|
Back To Top |
| |
|
Definition of the Surgical microscope |
operating
microscope - binocular microscope
(dentistry,operation) used into provide a clear view of small and
inaccessible parts of the body (as in microsurgery)
binocular microscope(dentistry,Operation) - a light microscope (Operation,dentistry) adapted to the
use of both eyes |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.thefreedictionary.com/operating+microscope |
|
Back To Top |
| |
|
How to Operate
a Microscope |
A microscope (Dental
surgical microscope, operating microscope,dentistry,
OperationSurgical microscope) allows a
specimen or sample to be magnified to a larger size so
that fine details can be examined. Taking the time to
prepare the microscope, and then focusing the microscope
properly are critical steps when using a microscope.
When done properly, looking at samples under a
microscope can be a fascinating experience.
Step 1
Before using the microscope (Operation,dentistry) , make sure it is plugged in
(if required). If the microscope does have an external
light source, turn it on. Prepare the specimen or sample
to be examined.
Step 2
Make sure that the scanning objective lens is in place.
Place the slide or sample under the microscope (Operation,dentistry). If
needed, use the stage clips to secure the slide in
place.
Step 3
Use the coarse adjustment knob to bring the sample into
focus. Depending on how large the specimen is, using the
fine adjustment may or may not help after initially
focusing using the coarse adjustment.
Step 4
Center the sample in the field of vision. Swing the low
power objective into focus. Again, use the coarse
adjustment followed by the fine adjustment to bring the
specimen into focus. If needed, adjust the light source.
Step 5
If the high power lens on the Dental microscope(dentistry,
Operation) is an oil
immersion lens, rotate the low power objective lens so
that the slide is easily accessible. Place a small drop
of oil on the slide directly over the specimen. Rotate
the high power lens into place.
Step 6
At this point, only use the fine adjustment knob to
bring the sample into focus. Using the coarse adjustment
knob can result in breaking the slide or damaging the
lens.
Step 7
When finished, be sure to rotate the scanning objective
lens into place before removing the slide. Clean the
lenses if needed, and turn off the power supply. |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.ehow.com/how_5145443_operate-microscope.html |
|
Back To Top |
| |
|
About Microscope
Basics |
Microscopes are one of
the most important tools in a laboratory. A microscope
(Dental
surgical microscope, operating
microscope,dentistry,Operation) can see objects that are not visible by the human eye
through its eyepiece and magnified objective lens. Most
students start with the compound microscope (dentistry,operation), which can
view small organisms such as amoebas and bacteria.
Eyepiece Lens
The eyepiece is used to see the object. It has
magnification associated with it, although it is not as
high as the objective lens. Most eyepieces have a
magnification power of 10-15x.
Illuminator
The illuminator is a small light that sits under the
stage. It shines a bright light onto the object for
better viewing.
The Stage
The stage is where the object is placed. It is directly
under the objective lens. The stage has controls that
slide it up or down and sideways to position the focal
point for observation.
Objective Lens
The objective lens is what gives the (Dental) microscope
(Dental surgical microscope,
dentistry,Operationoperating microscope.) its
power. There are four lenses which allow for 4X, 10X,
40X and 100X magnification.
Calculating Total Magnification
To calculate the total magnification that is seen
through the ocular (eyepiece) and the objective lens,
multiply the ocular and the objective. If your ocular
has a magnification of 10 and you use the 40X objective
lens, then the object you view is seen at 400X
magnification power.
Microscope Facts
History
Anton van Leeuwenhoek did not invent the microscope(Dental
surgical microscope , operating
microscope,dentistry,Operation) ,
though he did improve upon the original concept and
design to such a degree that he is frequently credited
with the microscope's creation.
Considerations
When a person looks through the eyepiece of a compound
microscope (dentistry,
operation), they are looking through two lenses, the
eyepiece lens and the objective lens.
Strength
The power of a microscope (Operation,dentistry) is generally displayed on the
scope. If a microscope has a 60x written on it, that
means the images you see will be 60 times larger than
they are in reality.
Calculation
The total strength of a microscope (Dental
surgical microscope,operating microscope, dentistry,
Operation) is determined by
multiplying the magnification of the lens in the
objective by the magnification of the lens in the
eyepiece.
Resolution
The resolution of a microscope refers to the distance
between two close objects that can still be
distinguished as separate. A microscope (Dental surgical microscope, operating microscope,dentistry,Operation.) is only as
useful as its resolution allows it to be.
Types
A microscope that has only one eyepiece is known as
monocular, while a microscope (dentistry,
Operation) with two eyepieces is
called binocular. Binocular are slightly more expensive
but are considered simpler for a beginner to use.
Proper Use and Care
of a Microscope (dentistry,
Operation)
Science progresses so
quickly at times that people tend to think nothing old
is good. Computers go from filling a room to fitting in
your lap. Scientists go from treating sicknesses with
"magic" potions to reprogramming the genetic code. But
there are some things that have been around for a long
time that remain just as relevant today as when they
were invented. The microscope (Operation,dentistry) is such a device. Handled
correctly and maintained, it still provides an
invaluable service.
Getting the Pieces in Place
A microscope (Dental surgical
microscope , operating microscope, dentistry, Operation) has many moving pieces, all of which can
help look at a specimen. To get started, a specimen is
put on a slide and the slide is set on the microscope
stage. The specimen should be placed over the center of
the glass circle, above the light below. The objective
lenses on a microscope (
operation,dentistry) offers three degrees of
magnification--scanning, low and high. The eyepiece also
has a magnification for fine tuning. To first look at
something on a slide, the scanning magnification should
be used. This is the lowest setting. Focus can be
adjusted by turning the coarse knob on the side of the
microscope (Operation,dentistry) to move the lens up and down. Center the
specimen as well as you can. Note here that, although
many people close one eye while looking into the
eyepiece, it is often recommended that you keep both
eyes open if you're going to do a lot of work with the
microscope (Dental
surgical microscope, operating
microscope,dentistry, operation). Doing so can help avert of eye strain.
Getting Closer
Once the scanning objective has focused on the specimen
as clearly as possible, you can move up one level to low
power. Again, turn the coarse knob to focus. You can
also use the finer focus on the eyepiece. Again, center
the specimen so that when you switch to high power, you
won't lose it.
Move up to high power, but here do not adjust with the
coarse knob. Doing so could scratch the lens. Adjust
only with the fine focus on the eyepiece. Throughout the
adjustments, you can also change the setting of the
diaphragm (directly below the slide) to let in more or
less light. Often, less light is better. Keep in mind
that everything you are seeing is in reverse--to move
something right in your view, you move the slide left.
To move it up, move the slide down.
Gentle Care
To keep the microscope (Dental
surgical microscope , operating microscope, dentistry,
operation) in good shape, always remove the
slide in the scanning objective position. Removing it in
high power can scratch the lens. When moving the
microscope, carry it by its arm.Wrap the electric cord
and put a cover over the microscope (Operation, dentistry). Wash any used
slides and dry them. Then put them back in the slide
box.
Cleaning a
Microscope
Objective Lens
Cleaning
To clean your microscope's (Dental
surgical microscope,operating microscope, dentistry,
operation) objective lens, dip some lens
paper into distilled water and wipe. If the lens is
still not coming clean, try mixing 1/2 cup of water with
an eye dropper full of household ammonia. Simply dip the
lens paper into the solution and wipe. Lens paper is
readily available at any photo store. For best cleaning,
use a circular motion from the inner part to the outer
part of the lens when wiping.
Eyepiece Lens Cleaning
If dirt that you see moves as you rotate your
microscope's(dentistry,
Operation) eyepiec, then the eyepiece lens is dirty.
To clean it, simply breathe on it until you see
condensation, and then wipe it with the lens paper. If
the lens is still dirty, dampen the lens paper with
rubbing alcohol and wipe over the lens surface. Use the
same circular motion as in Section 1 when wiping.
Cleaning the Body of the Microscope
Remove dust and dirt from the plastic or metal pieces
that make up the body of the microscope (Surgical
microscope,Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope, dentistry,operation.) with a damp
cloth. The cloth should be wet with water or with a mild
cleaning agent like Windex, 409, or any other household
cleaning products of this nature.
How Does a
Microscope Work?
A Bright Field
microscope (dentistry,Operation) is the most basic type of microscope
(Dental surgical microscope ,
operating microscope,dentistry,operation) almost everyone has seen or had the opportunity to play
with sometime in their lives. It consists of a plate
over which is suspended a tube. This tube contains an
eyepiece connected to an interior lens called an ocular.
The ocular is then connected to an objective lens, which
is the lens assembly that focuses and magnifies light
passing through it. Typically there are several lenses
on a circular dial which can be switched to see an item
at specific levels of magnification. A specimen is
placed on a perfectly transparent glass rectangle. It is
clipped into place on the center of the plate. Below the
glass is a hole in the plate, beneath which is a light
source. Cheap (Dental) microscopes (Dental
surgical microscope,operating microscope, dentistry,
operation) have mirrors, but professional
Bright Field microscopes include a light bulb. The light
bulb is turned on, the light passes through the glass
above it, through the lens, through the ocular, into the
eye of the observer. The image can be focused by means
of two dials on the sides of the microscope, which move
the tube back and forth until the lens in the ideal
distance from the specimen for the clearest picture
possible.
The Dark Field microscope is similar in
form and function to a Bright Field microscope (Operation,dentistry) . The main
advantage to this type of microscope is that it enhances
contrast between the specimen and surrounding bodies.
Inability to see where one organism or structure stops
and the other begins is the biggest problem with a
Bright Field microscope (Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope,dentistry,operation.). Light is emitted beneath the
sample as usual, but it does not have a straight line to
the sample plate. Instead there is a small disc in the
way which occludes some of the light, only letting light
pass around the disc. This light passes through a
condenser lens and is focused on the sample plate, which
it subsequently passes through. Some light, upon direct
contact with a solid object within the sample, is
scattered outward. That light is picked up while the
light which passed directly through the sample plate is
occluded by another disc called a direct illumination
block. The scattered light is passed through the lens,
is focused, and passed on up to the ocular for viewing.
A Fluorescence microscope (Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope, dentistry,operation) is a device used
specifically for examining organic specimens only. This
is because it relies on the intended specimen to react
to a specific wavelength of fluorescent light which is
typically beyond the capacity for the human eye to see.
The light is passed through a focusing lens, then
through the specimen. The specimen reacts by bending the
light, creating a slightly longer wavelength of light to
be reflected than that which was originally used. A
photosensitive lens is placed over the magnifying lens.
This lens is set to respond to a wavelength within a
range somewhat greater than that which was used. The
lens reacts to this wavelength by making the invisible
light visible to the human eye, making only the part of
the specimen one is interested in easily studied.
|
| Article Source: |
| http://www.ehow.com/facts_5191960_microscope-basics.html |
|
Back To Top |
| |
|
Operating microscope
|
| a binocular
microscope (dentistry,operation) used in delicate, especially of the eye or ear. The standing type of operation
microscope has a motorized zoom system operated by a
foot pedal that quickly changes the magnification. The
operating microscope that attaches to a surgeon's head
has interchangeable lenses for different magnifications.
Also called operation microscope(Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope, dentistry, Operation).
microscope
an instrument used to obtain an enlarged image of small
objects and reveal details of structure not otherwise
distinguishable.
acoustic microscope
one using very high frequency ultrasound waves, which
are focused on the object; the reflected beam is
converted to an image by electronic processing.
binocular microscope
one with two eyepieces, permitting use of both eyes
simultaneously.
bright-field microscope
the standard bench microscope (dentistry,Operation) used in histology and
requiring stained tissue sections.
compound microscope
the standard laboratory microscope (dentistry,operation,Dental surgical microscope, operating microscope) used in veterinary
science; consists of a two lens system whereby the image
formed by the system near the object (objective) is
magnified by the one nearer the eye (eyepiece).
darkfield microscope
used for examining unstained, often living cells, in
which light is only directed into the objective lens if
it is deflected by an object in its path. The object is
thus viewed as a white structure in an otherwise black (darkfield)
background.
electron microscope
one using an electron beam of very short wavelength as
the source of illumination. It has a resolving power of
2 nm (which is 100 times greater than with the light
microscope). Includes the transmission electron
microscope and the scanning electron microscope (below).
See also immunoelectron microscopy (dentistry,Operation)
fluorescence microscope
one used for the examination of specimens stained with
fluorochromes or fluorochrome complexes, e.g. a
fluorescein-labeled antibody, which fluoresces in
ultraviolet light. See also fluorescence microscopy.
interference microscope (Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope, dentistry,operation)
a microscope similar to the phase contrast microscope
but delivers a three-dimensional image. Called also
Nomarski interference phase microscope (dentistry,operation).
light microscope
used for examining unstained or stained particles or the
cellular structure of tissues that have been cut into
sections and stained. It has a resolving power of 0.2 μm.
Modern light microscopes have an eyepiece and objective
lenses which provide magnification, and a condenser
beneath the stage which gathers and focuses light on the
object being examined.
operation microscope
one designed for use in performance of delicate procedures, e.g. on the middle ear, eye or small vessels
of the heart.
phase microscope, phase-contrast microscope
a form of light microscope (Dental surgical microscope, operating
microscope, dentistry,operation) useful for examining living,
unstained structures, including animal cells and
bacteria, e.g. leptospira. The phase of the light wave
passing through different structures in the cell, e.g.
nucleus vs. thin part of the cytoplasm, is changed by
different amounts and thereby provides contrast.
polarizing microscope
based on the phenomenon of birefringence; useful in the
study of bone and muscle.
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
an electron microscope (Operation,dentistry) that produces a
high-magnification image of the surface of a
metal-coated specimen (shadow casting) by scanning an
electron beam and building up an image from the
electrons reflected at each point. Particularly useful
for determining the three-dimensional structure of
objects.
simple microscope (dentistry,Operation)
one that consists of a single lens.
specular microscope
one used in the examination of the corneal endothelium.
stereoscopic microscope
a binocular microscope (dentistry,Operation) modified to give a
three-dimensional view of the specimen.
see operating microscope (above) (Dental
surgical microscope , operating microscope, dentistry,
operation) .A binocular microscope
used to visualize fine structures within the area of a
procedure. Also called operation microscope.
transmission electron microscope, TEM
one that resembles an inverted light microscope in that
the beam of electrons generated from a heated filament
at the top of the instrument passes down through a
column where it is focused by magnetic coils (lenses)
and is differentially scattered when it passes through
the specimen. The image is recorded either on a
photographic plate or on a phosphorescent screen.
ultraviolet microscope (Operation,dentistry)
uses an ultraviolet light source; useful in
histochemical studies; only photographic images are
available. |
| Article Source: |
| http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/operating+microscope |
|
Back To Top |
| |
|
Surgical
Microscopes Summary |
Surgical
microscopes(Dental surgical microscope, operating microscope, dentistry, operation.)are one of the most
exciting advancements in the field. For more
than half a century, surgeons around the entire world
have been using microscopes to perform
intricate surgeries.
The concept of this tool was first pioneered by
Carl Zeiss - a leading German company in optical and
opto-electronic industry. The on humans under a
instrument was first performed in 1957.
surgery microscopes (Operation,dentistry) are very useful in getting a good
three dimensional visualization of the patient's
anatomy. The prime advantage of these microscopes is
that they feature coaxial injection of the light source.
They provide wide magnification ranges with good depth
of field. Two types of magnification changers are used
in the instrument: motorized or zoom system and
step system. Three and five step magnification changers
are the common ones. microscopes (Dental surgical microscope,operating microscope,dentistry,Operation) also meet the
best optic requirements such as high resolution and
bright illumination.
Different models of surgery microscopes (Operation,dentistry) are available.
Stand/floor type and table type models are the common
ones. Wall and ceiling mounted surgery microscopes are
the other models. High-quality portable
microscopes are widely used, especially for eye surgery.
The three premium models of the instrument include
the OPMI Vario/NC33 System (Carl Zeiss), the Leica M520
OH3 (Leica Microsystems), and the OME-8000 (Olympus).
All these three are used for spine
The high-end the instrument available today
incorporate a wide range of advanced features. Some
models come with an additional the instrument
camera. With this, the image produced by a
Dental microscope can be comfortably viewed on-screen during
the. Moreover, it helps to record the images.
surgery microscope
(dentistry,Operation) with speech recognition system is
one of the latest innovations. The voice activated
control system in the microscope will help to control
various functions like zoom, focus, and X-Y movements.
Microscopes provides detailed information on
Microscopes, Electron Microscopes, Parts of a
Microscope,Compound Microscopes (Dental surgical microscope,
operating microscope,dentistry,Operation.) and more. Microscopes
is affiliated with Reverse Osmosis Water Filter. |
| Article Source: |
| http://ezinearticles.com/?Microscopes&id=354571 |
|
Back To Top |
|
|



