|
|
 |
|
ENT Surgical microscope Knowledge Summary |
 |
|
We specialize
and sell in
manufacture that ENT surgical microscope .¡¡ |
|
¡öOperate
Microscope |
|
¡öThe
Dental
surgical Microscope |
|
¡ö
Microscopes Knowledge |
|
¡öWelcome
to surgical microscope(operate microscope) |
|
¡öMicroscope Buying Guide ¡ª Simple Steps to
Effective Microsurgery |
|
¡öThe
influence of the microscope in
locating the mesiolingual canal orifice: a laboratory
analysis |
| ¡¡ |
|
Model LZL-4D the Latest Light Multi-function Operation
Microscope
(ENT surgical microscope,Otolaryngology,Operation,operating)

¡¡ |
|
The influence of the surgical microscope
in locating the mesiolingual canal orifice: a laboratory
analysis |
| Operation microscope(surgical,Otolaryngology,
operating, Operation, ENT
surgical microscope) is a kind of microscope that is generally
utilized in medical surgeries that is performed on the
ear, nose and the throat. Another kind of microscope (surgical, operating, Operation)is utilized in performing of eye
operations by ophthalmic doctors. The most common
feature of a microscope is the
motorized foot controlled focusing, which can help the
physician to focus his hands on conducting the
rather than making use of it to adjust the focusing of
the microscope image. Operating microscope (ENT surgical microscope, operating,Operation,
surgical,Otolaryngology) is
an example of a stereoscopic microscope that has two
eyepieces. Other models of operation microscope
may have a zoom focusing capability and also with
multiple viewing heads that can be used for teaching or
for having another physician that is observing the
procedure.
In need of a surgery
microscope for an application such as Otolaryngology
microscope (operating,operation,ENT surgical microscope,surgical,otolaryngology),hand microsurgery , ophthalmic eye
surgery,or general micrology use? We can provide
the equipment you need.We have microscopes (surgical,Operating,Operation,
Otolaryngology) for
ophthalmology , ENT and general medical use with the
angled binocular head or straight head. We can add
optional accessories such a beam splitter to take the
image to a ccd camera port, which in turn is mounted a
ccd camera for output to a cctv display monitor. We can
also provide higher end units that have
assistant heads, also known as teaching heads. These
additional heads can be either binocular (with two
eyepieces) or monocular with a single viewing eyepiece.
Some specialized systems can have enough viewing
stations for up to three or four physicians and
assistants to simultaneously watch the micrology (operating,operation)
being performed. Please contact us today to discuss your
specific needs.
ABSTRACT
The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of
using the surgery microscope (SOM)(ENT,surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology,ENT
surgical microscope) for
detection of the mesiolingual (ML) canal orifice in
extracted first maxillary permanent molars. One hundred
and eight human first maxillary permanent molars were
randomly selected and mounted onto a dental chair
mannequin. Conventional access cavity was prepared and
an attempt was made to locate the mesiolingual canal
orifice using only a sharp explorer, a mirror and a #10
K-file. A mesiolingual canal orifice was either located
or not located. If not located, the teeth were then
evaluated by using a surgery microscope (Otolaryngology, ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation) (SOM).
The mesiobuccal roots of all teeth where the ML canal
orifice had not been located were sectioned in an axial
plane and the sections were explored with an adjunctive
use of the SOM at a 25 X magnification. ML canal
orifices were detected in 58 teeth using only a sharp
explorer, a mirror and #10 K-file. In the remaining 50
teeth, 37 ML canal orifices were located by using the
SOM and 3 ML canal orifices were located after root
sectioning.In 10 teeth,ML canal orifices were not
found.The results of this study showed a high incidence
of a ML canal in the mesiobuccal roots of the first
maxillary molars (90.7%) and demonstrated that the
adjunctive use of the SOM increased the ability of the
dental clinician to locate the ML canal orifice.
Descriptors: Incidence; Dental pulp cavity; Microscopy.(operating,operation)
INTRODUCTION (operating,ENT surgical microscope,surgical,Otolaryngology)
The goals of successful endodontics are the total
obliteration of the canal space and the perfect sealing
of the apical foramen with an inert filling material.
For this, the location and negotiation, with subsequent
cleaning and shaping, of the root canal system are
necessary . P¨¦cora et al.11 (1992) affirms that one of
the main reasons for the failure of root canal therapy
is the lack of sufficient knowledge concerning the
anatomy of teeth, both internal and external. The first
maxillary molar is the most bulky teeth in the mouth,
and has many anatomical variations. Usually both the distobuccal root and the palatal root present only one
canal. The mesiobuccal root presents more anatomical
variations, such as the number and disposition of the
canals. Bjorndal, Skidmore2 (1983) affirmed that the
difficulty in locating the mesiolingual canal (ML)
during the first maxillary permanent molar endodontic
treatment may have implications for the long-term
prognosis.
Clinically, the presence or absence of the mesiolingual
canal is limited by the conditions in which locating of
the orifice is carried out. The ability to locate the
mesiolingual canal depends on the skill of the operator,
the complexity of the anatomy and the use of high power
illumination and magnification techniques, such as that
performed with the operation microscope(operating,Operation,
ENT surgical microscope,surgical,Otolaryngology). A
literature review has demonstrated wide variation in the
prevalence of the ML canal mostly in in vitro
researches. Hess6 (1925), in a classical study, reported
finding 4 canals in 54% of first maxillary molars. Weine
et al.16 (1969) evaluated first maxillary molars and
located 4 canals in 62% of the teeth. Pineda, Kuttler12
(1972) evaluated the number of canals in first and
second molars and found 4 canals in 51.5% of the teeth.
Fogel et al.4 (1994) evaluated the use of 2.5 X
magnification telescopes with fiberoptic headlamps for
locating the mesiolingual canals in first maxillary
molars in vivo. They found that 71.2% of the mesiobuccal
roots had two canals. Stropko15 (1999) found 73% to 93%
of mesiolingual canals in a recent clinical study. Baldassari-Cruz et al.1 (2002) evaluated the influence
of the dental operating microscope(surgical,operating,Operation,ENT
surgical microscope, Otolaryngology,ENT) in locating the mesiolingual
orifice. This study demonstrated that the adjunctive use
of the dental operating microscope (surgical,operating,Otolaryngology, Operation)
increased the ability of the clinician to locate a mesiolingual canal.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether the
adjunctive use of the operating microscope
(surgical,Otolaryngology,operating,Operation) would increase detection of the mesiolingual canal
orifice in the mesiobuccal root of first maxillary
permanent molars.
MATERIALS & METHODS
For this study, 108 human first maxillary left and right
molars were selected randomly from the tooth bank of the
Department of Endodontics, Rio de Janeiro State
University.
The teeth were stored in 10% neutral formalin. The sex
and race of the patients from whom these teeth were
obtained were unknown. The teeth were mounted onto a
dental chair mannequin (Columbia Dentoform, Long Island,
NY, USA). No isolation of the teeth by rubber dam was
done. Without using magnification or headlamps, a
conventional access cavity was prepared using a #6
high-speed hand-piece spherical bur (Dentsply-Maillefer,
Ballaigues, Switzerland), a sharp endodontic explorer, a
mirror, a #10 K-file (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues,
Switzerland) and water irrigation. After locating the
mesiobuccal, distobuccal (surgical,operating,Operation,ENT
surgical microscope,Otolaryngology)and palatal canals, an attempt
was made to locate the mesiolingual canal orifice using
only a sharp explorer, a mirror and a #10 K-file. If the
mesiolingual canal orifice was not located, a #700l
low-speed hand-piece bur (Dentsply-Maillefer, Ballaigues,
Switzerland) was used 2 or 3 mm into the orifice of the
mesiobuccal canal where a trench was prepared in a
lingual and slightly mesial direction through the mesial
dentinal shelf1. The root was again explored by using
only a sharp endodontic explorer, a mirror and a #10
K-file in an attempt to locate a mesiolingual canal
orifice.
A mesiolingual canal orifice was either located or not
located. If not located the teeth were then evaluated by
using a operating microscope (Dental F. Vasconcelos, M900 ¨C25 X, São Paulo,Brazil)
(urgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology,ENT
surgical microscope)
at a
magnification of 25 X. Again, an ML canal orifice was
either located or not located. The mesiobuccal roots of
all teeth where the ML canal orifice was not located
were sectioned in an axial plane 6 mm below the cemento-enamel
junction. The sections were explored using a sharp
endodontic explorer, a mirror and a #10 K-file (Figure
1F) with the adjunctive use of the surgery
microscope(surgical,operating,Otolaryngology,Operation)at a magnification of 25 X to determine the
actual presence or absence of the orifice of the ML
canal. In this methodology, each tooth served as its own
control.
RESULTS
In the first phase of this methodology, with the use of
only a sharp endodontic explorer, a mirror and a #10
K-file (unaided vision), a total of 58 ML canal orifices
were detected out of 108 teeth (53.7%). The 50 teeth
where the ML canal orifices could not be located with
unaided vision were submitted to evaluation under a microscope (SOM)(ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,Otolaryngology,operating,Operation). After this
evaluation, a total of 37 ML canal orifices were located
(74%). Thus, 37 ML canal orifices could only be located
with the use of the SOM. In the lab, after sectioning, 3
additional ML canal orifices were located in the
remaining 13 teeth (23%). These 3 canals were located
neither with the traditional methods nor with the SOM
evaluation. A total of 98 ML canal orifices were
identified out of 108 experimental teeth (90.7%). (Graph
1).
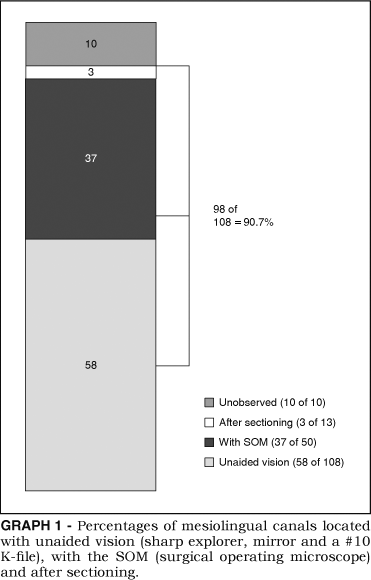
Figure 1A shows one of the first maxillary molars (operating,operation) used
in this experiment and the presence of 4 distinct
foramina (Figure 1B). Figure 1C shows an example of the
difficulty in locating the ML canal orifice in the first
maxillary molar, and Figure 1D summarizes the results of
this work.
DISCUSSION
The results of the present study demonstrate that 53.7%
of the ML canal orifices were detected by using a sharp endodontic explorer, a mirror and a #10 K-file. With the
adjunctive use of the SOM, the incidence increased from
53.7% to 87.96%. This result showed the efficacy of this
clinical procedure. Carr3 (1992) affirms that the
operation microscope(surgical,operating,ENT
surgical microscope,Otolaryngology, Operation) has greatly improved the ability of
the endodontist to visualize and treat periapical
pathology in endodontic . It has also enhanced
the practice of non endodontics. The higher
magnification and illumination can be useful for access
cavity preparation, instrumentation and obturation. It
can improve the clinician's view of the complexity of
the root canal anatomy and aid in the location of
additional canals, fins or ribbons. Thus, the use of the
SOM to detect the ML canal orifice of first and second
maxillary molars may enhance the success of endodontic
procedures.
Conservative or small access cavity preparations are not
recommended because some missed canals can lead to root
canal therapy failure. Weller, Hartwell17 (1989) have
stated that there is an increased probability of finding
the mesiolingual canal if the initial access is changed
from a classical triangular shape to a more rhomboidal
shape. Modification of the access cavity (to a
rhomboidal shape) to include a trench preparation from
the mesiobuccal canal to a mesiopalatal (Operation,operating,Otolaryngology) direction, where
the ML canal orifice may be typically found, increases
the frequency of ML canal orifice detection. Once a
rhomboidal access shape has been established and all
major canals have been located, a careful examination of
the pulpal floor should be conducted. Baldassari-Cruz et
al.1 (2002) related that different access cavity shapes
increase the frequency of locating the ML canal in the mesiobuccal root of the first maxillary molar.The surgical microscope(surgical,ent
surgical microscope , Operation,operating,Otolaryngology) is very useful in
performing this task. Combined with the knowledge about
root canal system morphology and accessibility, enhanced
vision to the area allows the operator to achieve
maximum results. This is confirmed by the high
prevalence of the ML canal orifice found in this study.
The negotiation as well as the cleaning and shaping of
the ML in the mesiobuccal (surgical,operating,Operation,ENT
surgical microscope,Otolaryngology)roots of first maxillary
permanent molars was not part of this study. We believe
that a great number of these canals are impossible to be
treated by methods used in endodontics nowadays. This
represents an interesting theme for future researches.
CONCLUSION
Our study showed a high incidence of the ML canal in the
mesiobuccal(operating,operation) roots of first maxillary molars (92%) and
demonstrated that the adjunctive use of the SOM
increases the ability to detect an ML canal orifice. |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1806-83242006000100011 |
|
Back To Top |
| ¡¡ |
|
The Dental
surgical microscope
(ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical,operating, Operation,Otolaryngology) |
While magnification in
general undoubtedly offers many benefits to both the
practitioner and patient,dental loupes do have some
distinct limitations associated with them when compared
to microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,
Otolaryngologysurgical, operating, Operation),the most obvious being that loupes are
restricted to a single level of magnification.
Additionally, by design, loupes are a convergent lens
optical system, which basically means that the
clinician¡¯s eyes must converge to view the operative
field, possibly resulting in eyestrain and fatigue,especially at higher levels of magnification or after prolonged periods of use. With loupes, as the level of
magnification increases so does their weight as well as
the need for an adjunctive light source to help improve
visualization, which further adds additional weight to
the system which, in turn, can result in increased
strain and fatigue of head, neck,and back muscles after
prolonged use.Compared to microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology)
, however, the
limitations of loupes are dramatically offset by their
significantly lower cost and ease of portability.
Despite their higher price tags, however, when the
dental microscope (surgical, operating,
ENT
surgical microscope,Otolaryngology,Operation ) is fully integrated into a
practice and used to its fullest potential, a return on
investment can be realized rather quickly. The three key
factors which contribute to a microscope¡¯s
income-generating ability is increased visualization,
digital documentation capabilities, and improved
ergonomics.
Advantages and Benefits of Dental Operating
Microscopes
(operating,surgical,
Otolaryngology,ENT surgical microscope,Operation)
Increased Visualization
In addition to having up to six levels of magnification
ranging from 2x to 20x available at one¡¯s fingertips,
illumination is a critical component in increasing
visualization. Most microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology) are equipped with an
integrated coaxial light source that allows for
unobstructed, shadow-free illumination of the OPS
field. With coaxial illumination, the path of light is
directed parallel to the microscope¡¯s (surgical,operating,Operation) optical axis,
which allows for significantly improved visualization of
even the most difficult to access areas of the oral
cavity.
With enhanced visualization, the clinician¡¯s ability to
diagnose problems in the earlier stages of a disease
process is possible. Treatments also can be performed
with a greater level of precision, thereby reducing the
occurrence of failures and the need for redos. Enhanced
visualization can also allow for treatment to be
provided more comfortably to the patient because of
lighter, more refined hand movements which occur
naturally when one is accustomed to OPS (surgical,operating,Operation) in a
well-illuminated magnified field. Increased
visualization can ultimately result in greater
efficiency and productivity because less time is wasted
with tactile exploration and confirmation that all decay
has been removed. When one can see all areas of the
mouth or of a preparation perfectly,the level of
efficiency and precision in diagnosis and treatment
naturally increases.
Digital Documentation Capabilities
This is perhaps the most significant advantage that
microscopes(ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical,operating,Otolaryngology,Operation)offer over loupes, and where a significant
return on investment can potentially be realized
provided that they are fully integrated and used to
their fullest potential. With the optional addition of a
beam-splitting device, one is able to integrate various
types of digital recording devices, such as an SLR
and/or video camera. Digital (Operation,surgical,operating,Otolaryngology) documentation capabilities
enable the clinician to efficiently capture and share
with patients what is seen during an examination
preoperatively, intraoperatively, and postoperatively.
During treatment, images can be efficiently captured,
shared, and stored in the patient¡¯s chart. This is
especially useful when unforeseen problems are
encountered. This not only helps to increase a patient¡¯s
level of trust and confidence in the treating doctor
(especially with newer patients), but can also aid in
reducing one¡¯s medical-legal risk.
Additionally, a live video source can be attached to the
microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,
Otolaryngology,operating,Operation) and fed to a TV or computer monitor,
strategically positioned so that it can be easily viewed
by the dental assistant. When the assistant is able to
see exactly what is being done during a procedure, not
only does his or her level of efficiency increase, but
the level of interest and motivation also rises
dramatically since he or she tends to feel more involved
during the procedure.
Once treatment is completed, a great way one can
internally market one¡¯s practice is by providing
patients with preoperative, intraoperative, and
postoperative color photographs of their treatment. This
has the great potential of stimulating new patient
referrals of friends and family members.
Improved Ergonomics
With dental microscopy(surgical,operating,ENT
surgical microscope,
otolaryngology,
operation), improved ergonomics is realized
on many levels, the most obvious being improved posture.
By OPS in a more upright, comfortable posture, the
operator is less likely to experience strain or fatigue
of neck and back muscles and is, therefore, able to work
comfortably for extended periods of time. This can
enable the practitioner to provide more dentistry in
fewer visits, increasing the clinician¡¯s productivity
and making for very happy patients. Ergonomics is also
improved during digital documentation because intraoperative images can be captured very efficiently
by the assistant so that the clinician does not have to
stop treatment.
Integrating Dental Operating Microscopes (Otolaryngology,ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical, operating, Operation)
The successful integration of any technology usually
requires a commitment of time and sometimes money.
Motivation (Operation,operating,Otolaryngology)and persistence are also key ingredients for
successful integration of technology. As is the case
with any new technology or procedure, formal hands-on
training will significantly decrease the amount of time
required to attain complete, successful integration. It
is important to realize that when incorporating anything
new to one¡¯s practice that problems will arise along the
way. To minimize the occurrence and frequency of
potential problems and ensure that the integration
process proceeds smoothly, an implementation plan is
critical.
The procedural execution plan involves making a list of
specific procedures organized by degree of difficulty
with the simplest being performed first. In the case of
dental microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology), the arch and area of the
mouth also needs to be taken under consideration. For
instance, with microscopes, the maxillary arch and
anterior segments of the oral cavity are the easiest to
start with. A crown preparation on a lower second molar,
for instance, may not be a desirable procedure or
location of the mouth to start with.
An example of an acceptable procedural execution plan
for a restorative dentist learning to integrate dental
microscopy(ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,
Otolaryngology) might include starting out with simple
filling restorations in the facial anterior segments
because this is the easiest area to visualize through
direct vision. One should preferably start out using the
lowest to low-medium powers of magnification before
advancing to higher powers of magnification to allow
sufficient time for one¡¯s hand-eye coordination to adapt
to OPS (Operation,operating,Otolaryngology) under a magnified field. Once a point is
reached where one feels comfortable in working under
various levels of magnification in the facial anterior
segments of the oral cavity, he or she can then proceed
to crown or veneer preparations on the maxillary
anterior segments where the use of a mirror would be
necessary. As the use of the mirror becomes integrated
with the use of a microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology) in the anterior maxillary
region, one can then advance posteriorly on the
maxillary arch only, until an adequate level of
proficiency is reached. The posterior mandibular region
is generally considered to be the most difficult area of
the mouth for an inexperienced microscope (surgical,operating,Operation) user to
operate in and should, therefore, be avoided during the
very early stages of the integration process.
While OPS with a microscope(ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operation, Operating,
Otolaryngology) does involve a bit of
a learning curve, the author personally has not found it
to be as difficult as some may perceive it to be; it
only requires practice, persistence, and time. As
mentioned earlier, formal training would help in
significantly reducing the amount of time needed to
fully integrate microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,Operating,Operation,
Otolaryngology)
into a practice and may be well worth the additional
cost for many new users or existing owners who have not
been able to successfully integrate microscopes fully. A
formal training course may also be a very valuable
learning experience for those just contemplating adding
dental microscopy (ENT
surgical microscope)to their practices before making an
actual purchase. Dental microscopy (operating,operation,ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,Otolaryngology)may not be suitable for everyone, but until
one tries, one may never know what they have been
missing. |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.insidedentistry.net/article.php?id=3290 |
|
Back To Top |
| ¡¡ |
|
Welcome to
Surgical Microscope |
The advancement of
technology has taken us to places we¡¯ve only dreamed of
before. It has taken us to the farthest of planets and
also to the tiniest microscopic (surgical, operating,
operation,Otolaryngology,ENT
surgical microscope) beings that we see
today. New technologies have helped in more ways than
one to keep ourselves enjoying the good things in life.
The greatest that these technologies have helped us is
in the medical and field where they give light
to disease that were at first were just myths or
diseases that we have misunderstood. The use of these
modern technologies have made us gain new information¡¯s
on how to treat or deal with these illnesses, avoid or
prevent such disease in occurring to us by means of medical operations.
The OPS (surgical,Operating,Operation) and field found in typical
hospital is the most environmentally controlled area
since there is a higher risk of infection. And with the
advancement of procedures there¡¯s
also an increased need of more advanced medical
equipment to cater these medical needs. And one of this
equipment is what we call the operating microscope (surgical, operating, Operation,ENT,OPS,
Otolaryngology,ENT
surgical microscope), a
microscopic device made to answer the growing and more
complex procedure. When it comes in
operation, equipments like operation microscope is much
needed to enhance the view of the surgeons for
microscopic structures like blood, lesions, and
lymphatic vessels. This is vital since magnification is
very much necessary for medical OPS. According to
a research, microscope (Operation,ENT surgical microscope, surgical, operating,Otolaryngology) is needed for
procedures in which the surgeon requires adjustable
focusing capability and greater stability than offered
by a loupe.
With the aid of microscope (surgical,Operating,Otolaryngology,Operation) surgeons all over
the world have the confidence to treat any patient as
well as speed up the recovery of the patient. Engineered
with precision,operation microscope(surgical,operating,Operation,
ENT surgical
microscope,otolaryngology)with its multiple
eyepieces allows surgeon to simultaneously view the
magnified area with ease and comfort. Another
interesting detail of surgery microscope is the
microscope drape; this is used to create a sterile
barrier which is initially affixed to the microscope (ENT
surgical microscope). A
typical ceiling mounted device, surgery microscope can
be raised or lowered and positioned over any part of the
patient¡¯s body for operation. |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.operating-microscope.com/ |
|
Back To Top |
| ¡¡ |
|
Operate Microscope
(Operating,Operation) |
| The field of surgical
microscopy encompasses a wide variety of applications,
along with the various equipment used for
these applications. The surgery microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology) is
a standard tool used in the room. Medical
procedures vary, creating the need for specialized
microscopy equipment to be tailored to the ind ividual
needs. Eye surgery is performed by ophthalmologists. The
ophthalmic microscope is typically with a binocular head
that is angled. Otolaryngology medical doctors on their patients.
The ENT
microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,
Otolaryngology, Operating, Operation, )is normally with a straight (no angle)
binocular head. Focal distances vary, so the bottom
objective lens is typically different depending on if
the application is for ophthalmic use or for ENT
surgical microscope (surgical,Operating,
Operation)/dental
use. Dental physicians use the dental microscope for a
variety of operation procedures inside the
mouth. Neurosurgeons, sometimes called brain surgeons,
use a microscope generally similar to an ENT operation
microscope (surgical,operating, Operation).
Various optional accessories and features can be ordered
with an operation microscope(surgical,operating,ENT
surgical microscope,Operation,Otolaryngology). Most higher end equipment
will come standard with motorized foot controlled
focusing for hands-free focusing. Some units have the
ability to center the field of view with motorized
controls, as well as tilt the angle of the head assembly
via servo motors. Eyepieces are usually 10x but
sometimes 12.5x. The typical objectives (bottom lens)
are f200 and f250. For more special applications, most
factories make the f300, f350, and f400 objective lens.
These change the focal distance, and result in different
magnifications and different working distances.
Some surgery microscopes
(surgical,operating,ENT
surgical microscope,Operation,
Otolaryngology) microscope have only a single binocular head, but more
advanced units have the option for teaching heads, also
called assistant heads. These additional heads allow
multiple simultaneous viewing of the patient by several
physicians. Most operations (surgical,Operation,Operating) do need assistants
who view the OPS (Otolaryngology,
operating,Operation)procedure. Also, physicians in
training are allowed to use these ¡°teaching heads¡±. Some
assistant heads are binocular, viewing the same image at
the same magnification as the master surgeon. They may
also be monocular with only one ocular eyepiece. Some of
the binocular teaching heads have ind ependent
magnifications.
Video microscopy (Operating,
Operation,Otolaryngology) is also an added feature in a surgery
microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,
Otolaryngology). Many of the models have optional
beam splitters to split the image to an optional c-mount
where a ccd camera can attach. These ccd cameras have
NTSC or PAL video output signals to be taken to a CCTV
viewing / display monitor. This video microscopy
equipment makes an excellent options package as it
allows multiple simultaneous viewing by all physicians
and assistants in the room.
If the operation microscope (surgical,operating,ENT
surgical microscope,Operation,
Otolaryngology) is to
be used in a hospital located in USA , then it needs to
be a US FDA certified model. Some of our models, but not
all, have FDA certification. All of our models have at
least the CE certification for Europe . Some countries
don¡¯t require any certification. But all customers
demand a reasonable level of quality and a good
discounted price. We can provide you what your hospital
or clinic needs, and at a significant savings over other
operating microscope (surgical,Operation,Operating) dealers. Please contact us today
for more details. |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.operatingmicroscope.com/ |
|
Back To Top |
| ¡¡ |
|
Surgical
Microscopes Knowledge |
 There
are various types of operation microscopes that are used for
different applications. One common type of operation
microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology)
is used by ENT surgical microscope (otolaryngology,
operating, operation) medical doctors. The binocular
head of the microscope is straight without any angle.
Also, the focal length is usually different. The focal
length of a microscope (otolaryngology,operation,
operating) is changed by simply
screwing on a different bottom lens under the head. This
also will change the overall magnification. Another
common type of microscope
for applications is
used by ophthalmologists for
correcting problems with the human eye. The binocular
head of this microscope is on
a 45 degree angle and the focal length is usually
different from equipment for
ENT surgical microscope(ENT
surgical microscope,surgical, Otolaryngology,operating,Operation)
usage. There are also microscopes for general
such as hand micrology,
orthopedic surgery, brain and neuro micrology, dental,
and other micrology
applications relating to human medical needs. There
are various types of operation microscopes that are used for
different applications. One common type of operation
microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology)
is used by ENT surgical microscope (otolaryngology,
operating, operation) medical doctors. The binocular
head of the microscope is straight without any angle.
Also, the focal length is usually different. The focal
length of a microscope (otolaryngology,operation,
operating) is changed by simply
screwing on a different bottom lens under the head. This
also will change the overall magnification. Another
common type of microscope
for applications is
used by ophthalmologists for
correcting problems with the human eye. The binocular
head of this microscope is on
a 45 degree angle and the focal length is usually
different from equipment for
ENT surgical microscope(ENT
surgical microscope,surgical, Otolaryngology,operating,Operation)
usage. There are also microscopes for general
such as hand micrology,
orthopedic surgery, brain and neuro micrology, dental,
and other micrology
applications relating to human medical needs.
Most microscopes(surgical,operating,Otolaryngology,ENT
surgical microscope,operation) for have motorized foot
controls for at least the focusing
of the image to free up the surgeon¡¯s hands for holding
the medical tools. The
higher grade equipment has additional foot controls for
movement of the head. Some
motorized controls are located on the head assembly
itself, and control rotation of
the head in multiple degrees of rotation as well as
centering the optics on the
area of interest.
A common optional accessory on a microscope(ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical, operating,Operation,Otolaryngology)
is the inclusion of multiple
heads for simultaneous viewing. Medical surgeons often
use assistant doctors and
nurses during the procedure. These assistant
heads are also good for
medical students for educational purposes. For student
use in a medical school, the
extra viewing head would be termed a teaching or
training head. If used during
by a medical professional assisting the lead
surgeon, the extra head would
be termed an assistant head.These assistant heads
(teaching heads) can be
monocular with only a single eyepiece, or binocular with
two eyepieces. They may see the exact magnification as the lead surgeon¡¯s
binoculars, or they may have
independent magnification controls. Higher grade medical microscopy (ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical, operating,Operation,
Otolaryngology)equipment will often have multiple assistant heads
allowing simultaneous viewing
for as many as three medical staff members in the
room.
Another optional accessory on a surgery microscope
(ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical, operating,operation,Otolaryngology)
is the use of video
display. A system can be fitted with a beam splitter and
c-mount for connection to
a ccd color video camera. This type of microscope camera
will output a composite
video signal to a cctv video monitor for all medical
personnel in the
room to see. The video of the can also be
recorded on standard video
recording devices.
A significant factor to consider when purchasing a operation microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,operating,Operation,surgical,Otolaryngology) is
the quality of the equipment and certifications held by
the manufacturer. As this
equipment is to be used in a medical / clinical setting,
many countries require
certification or registration of the equipment or
manufacturing facility. In the
USA , the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA)
registers manufacturing
facilities that make medical products. If the equipment
you need is for a USA location, then you need one of our surgical microscopes (surgical, ENT
surgical microscope,operating,Operation,
Otolaryngology)
that is made in an FDA
registered manufacturing facility. We carry
medical equipment from both
FDA and non-FDA registered manufacturers. For locations
such as in Europe , the CE
certification is required for medical devices. We also
can provide CE certified equipment. For some countries, no certification
or FDA registration is
required. We can provide lower cost surgery microscopes
(surgical,
Operation,Operating) to these other countries
not needing certification.
Our selection of surgery microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,
operating, Operation,Otolaryngology) is wide,
allowing the medical
doctor to choose from many different types, with
different optical features,
different grades of quality, and with or without FDA
manufacturer registration / CE certification.
Our prices on these vary, but you can be
assured our prices are
competitive, and generally lower than anyone else
selling identical
equipment. Please contact one of our sales
agents today for more details
on our microscopes. (surgical,
operating, Operation,
Otolaryngology, ENT
surgical microscope, ) |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.operatingmicroscopes.com/ |
|
Back To Top |
| ¡¡ |
|
Surgical Microscope Buying Guide ¡ª Simple
Steps to Effective Microsurgery
(Operating,Operation) |
The practicality and
innovation that surgical microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology) bring
should not be underrated. They make operations
possible even if it means beyond the capabilities of the
usual medical techniques. However, before you buy a
surgery microscope, there are quite a few
factors that you should consider. Learn these all from
this surgery microscope (surgical,
Operation,
Operating) buying guide.
An Overview
However, there are times that is employed to
find the problem itself. For instance, a surgeon, one
who specializes in the field of , may have to
remove a section of tissue, the process also known as
biopsy, from the body for analysis or tests. The tissue
will be analyzed using a microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,
Otolaryngology) to support needed
information in diagnosis.
At this point, let us introduce surgical microscope.
For simple examinations of tissues or cells that are
normally scraped off from the body since the procedure
will no9t require bigger samples, typical
microscopes (surgical,Operation,Operating) are used. On the other hand, more advanced require advanced
microscopes that can facilitate the OPS. Advanced OPS microscopes (Otolaryngology,
operating,Operation) provide three-dimensional
image of the patient¡¯s structure. The major benefit of
these particular microscopes is that they highlight
¡°coaxial injection¡± in the illumination section. They
offer good depth of field and wide magnification ranges.
Moreover, microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,Operation,Otolaryngology) are endowed
with the best optic requirements such as bright
illumination and high resolution.
With this feature,advanced models of microscopes (surgical,operating,operation) are developed and are used for more advanced procedures. There are different types of
surgical microscopes: wall and ceiling mounted
microscopes, table type models, floor
or stand types, and high-quality handy microscopes (surgical,operating,Operation).Each type has its own function. For example, handy
microscopes are used for eye
such as cataract .
Given the fact that advanced technologies, such as
digital technology, are available in the market today,high-end microscopes(ENT
surgical microscope,surgical,operating,
operation,Otolaryngology)are now being developed and made
available in the market. Some operating
microscopes are now equipped with digital or video
cameras for better quality image and documentation.
Moreover, incorporating digital technology in microscopy(operating,Otolaryngology
,Operation), presentation or analysis of observations is
easily viewed on screen or in a television.
Buying Guide
The major critical element in micrology is the microscope(operating,operation).Microscopes (Otolaryngology,
operating,Operation) of this type
are available in a wide range of features and
manufacturers based on their particular application.Generally, all types of operating microscopes(Otolaryngology,
operating,Operation)
share common attributes.However,it is till important
to learn how to choose the right
microscope designed specifically for certain types of
surgeries. You really do not have to be meticulous in
choosing operating microscopes.(operating,ENT
surgical microscope,Otolaryngology, surgical,
operation) You just have
to consider some important factors just to identify
specific operating microscopes for a specific
function.
Illumination
In buying microscopes (operating,Otolaryngology,Operation) , always try to
consider the light source. Keep in mind that microscopy
deals with certain concepts only to project or
demonstrate image as seen by the eyepieces. Without
proper illumination, images will not be seen clearly.
Standard microscopes (surgical,
Otolaryngology, ENT
surgical microscope, operating, Operation) use different types of light
sources. The most common are fluorescent, tungsten, and
halogen bulb. Among the three, fluorescent bulb systems
are considered to be the best light source that can be
used in a microscope (surgical,Operation,Operating) . This type of
light source produces less heat and supply brighter
illumination as compared to halogen or tungsten.
Structure
Durability is an essential factor when considering a microscope
(surgical,operating,
Operation ). Only buy a microscope
(operating,Operation,Otolaryngology) that is firmly constructed and made
up of hard-wearing metal alloy.
Classification
Since there are many types of microscopes (ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical, operating, Operation,Otolaryngology), it is best
that you buy a stereo microscope for
operations. Ster depth perception even though its
magnification and resolution is low.reo microscopes are
capable of providing three dimensional images, which
will provide highe
Types of specimen
Before you buy a operating microscope (ENT
surgical microscope,
surgical, operating, Operation,Otolaryngology), it is
important that you know exactly the kind of specimen you
will be observing. Some microscopes
may not work with the other kinds of
microscopes. For instance, microscope
used in cataract can be entirely different with
that of the other types to be used in other
operations.
Boiled down, following this
microscope (operating,Otolaryngology,Operation) buying guide can help you avoid waste of
time, money, and effort. |
| Article Source: |
| http://www.microscope.com/operating-microscope-buying-guide-simple-steps-to-effective-microsurgery.html |
|
Back To Top |
|
|



